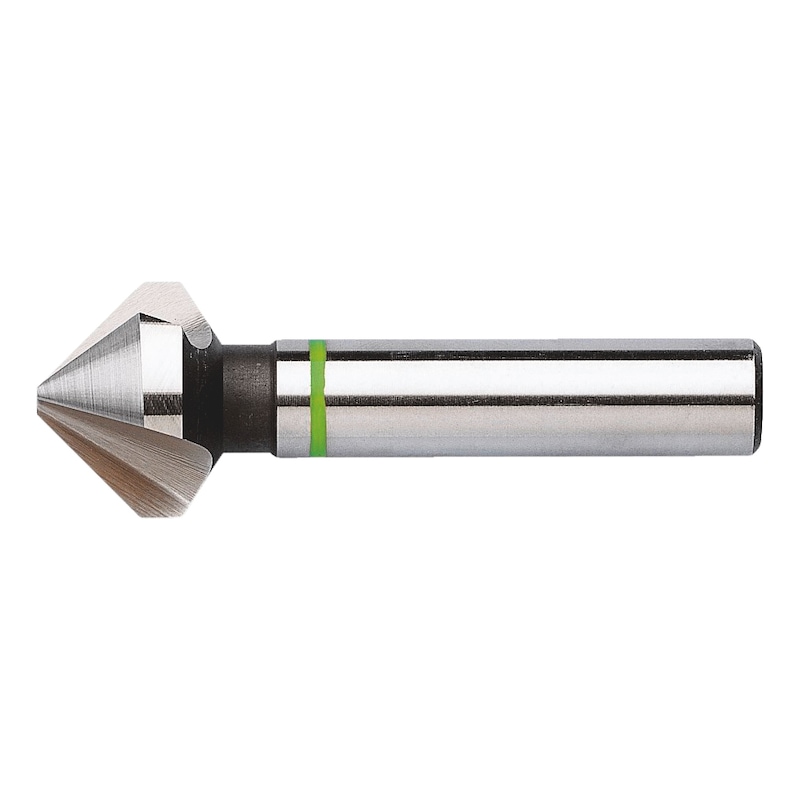
HSCo 90° green-ring countersink DIN 335C
Conical countersink HSCo, green ring
CNTSNK-CONI-MA-GREEN-HSCO-90DGR-D31MM
Art.-no. 069401931
EAN 4011231603423


Register now and access more than 125,000 products
Burr- and chatter-free countersinking and deburring
Precision conical countersink with three cutting edges, precision-ground
Optimised flute geometry
Excellent chip formation and removal
Product packaging made from 100 % PCR (recycled plastic from household waste) and 100 % recyclable
Datasheets(X)
 | |
Material to be processed | Steel, Cast metal, Stainless steel, Titanium, Special alloy |
Quality | ZEBRA-Premium |
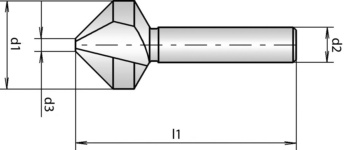
Spot-facer diameter (d1) | 31.0 mm |
Shank diameter (d2) | 12 mm |
Tip diameter (d3) | 4.2 mm |
Length (l1) | 71 mm |
Number of cutting edges (Z) | 3 PCS |
Standards | DIN 335 |
Form | C |
Cutting material | HSCo |
Countersink angle | 90 Degree |
Surface | Uncoated |
Shank style | Cylindrical |
Service life (points system) | 2 of 4 points |
Countersinking speed (point system) | 2 of 4 points |
Countersinking quality (point system) | 2 of 4 points |
Versatility (points system) | 2 of 4 points |
Countersinking behaviour (point system) | 2 of 4 points |
Material of sub-group | General structural steels, Non-alloyed tempering steels, Alloyed tempering steels, Nitriding steels, Tool steels, High-speed steels, Cast iron, Ductile iron, Malleable cast iron, White cast iron, Stainless steels, sulphurated, Stainless steels, austenitic, Stainless steels, martensitic, Titanium, Titanium alloys, Special alloys, Spring steels |
| Assignment of conical countersink to screw standards | ||
| Conical countersink nominal diameter d1 | For countersunk head screws | For countersunk head screws |
| DIN EN ISO 10642 (formerly DIN 7991) | DIN EN ISO 2009, 2010, 7046, 7047 (formerly DIN 963,964,965,966) | |
| 6.3 mm | M3 | M3 |
| 8.3 mm | M4 | - |
| 10.4 mm | M5 | M4, M5 |
| 12.4 mm | M6 | M6 |
| 16.5 mm | M8 | M8 |
| 20.5 mm | - | M10 |
| 25.0 mm | M10, M12 | M12 |
| 31.0 mm | M16 | - |
| Legend |
| vc = cutting speed [m/min] |
| f = feed (mm/r) |
| The suggested cutting values are reference values and must be adapted to the respective conditions. |
| For dia. 16.5-31 | ||||||
| Material designation | Tensile strength | vc | f | |||
| Dia. 16.5 | Dia. 20.5 | Dia. 25 | Dia. 31 | |||
| Steels | ||||||
| General structural steels | ≤ 500 N/mm² | 35 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 |
| ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 33 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 | |
| Unalloyed quenched and tempered steels | ≤ 700 N/mm² | 35 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 |
| ≤ 850 N/mm² | 33 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 | |
| ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 22 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 | |
| Alloyed quenched and tempered steels | ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 17 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 13 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 | |
| Nitriding steels | ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 17 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 13 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 | |
| Tool steels | ≤ 850 N/mm² | 19 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 17 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 | |
| High-speed steels | ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 17 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,150 | 0,120 |
| Stainless steels | ||||||
| Sulphurated stainless steels | ≤ 900 N/mm² | 18 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 |
| Austenitic stainless steels | ≤ 1,100 N/mm² | 13 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 |
| Martensitic stainless steels | ≤ 1,200 N/mm² | 15 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 |
| Titanium and titanium alloys | ≤ 850 N/mm² | 17 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 11 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 | |
| Special alloys | ≤ 1,600 N/mm² | 9 | 0,110 | 0,130 | 0,150 | 0,170 |
| Cast metals | ||||||
| Cast iron | ≤ 240 HB | 28 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 |
| ≤ 350 HB | 18 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 | |
| Spheroidal graphite and malleable iron | ≤ 240 HB | 24 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 |
| ≤ 350 HB | 22 | 0,170 | 0,180 | 0,210 | 0,240 | |
| Chilled cast iron | ≤ 350 HB | 9 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 |
| Hard materials | ||||||
| Spring steels | ≤ 350 HB | 11 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,120 |
| Cutting values | ||||||
| For dia. 6.3-12.4 | ||||||
| Material designation | Tensile strength | vc | f | |||
| Dia. 6.3 | Dia. 8.3 | Dia. 10.4 | Dia. 12.4 | |||
| Steels | ||||||
| General structural steels | ≤ 500 N/mm² | 35 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 |
| ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 33 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 | |
| Unalloyed quenched and tempered steels | ≤ 700 N/mm² | 35 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 |
| ≤ 850 N/mm² | 33 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 | |
| ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 22 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 | |
| Alloyed quenched and tempered steels | ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 17 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 13 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 | |
| Nitriding steels | ≤ 1,000 N/mm² | 17 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 13 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 | |
| Tool steels | ≤ 850 N/mm² | 19 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 17 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 | |
| High-speed steels | ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 17 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 |
| Stainless steels | ||||||
| Sulphurated stainless steels | ≤ 900 N/mm² | 18 | 0,068 | 0,081 | 0,090 | 0,100 |
| Austenitic stainless steels | ≤ 1,100 N/mm² | 13 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 |
| Martensitic stainless steels | ≤ 1,200 N/mm² | 15 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 |
| Titanium and titanium alloys | ≤ 850 N/mm² | 17 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 |
| ≤ 1,400 N/mm² | 11 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 | |
| Special alloys | ≤ 1,600 N/mm² | 9 | 0,070 | 0,080 | 0,090 | 0,100 |
| Cast metals | ||||||
| Cast iron | ≤ 240 HB | 28 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 |
| ≤ 350 HB | 18 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 | |
| Spheroidal graphite and malleable iron | ≤ 240 HB | 24 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 |
| ≤ 350 HB | 22 | 0,120 | 0,130 | 0,140 | 0,150 | |
| Chilled cast iron | ≤ 350 HB | 9 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 |
| Hard materials | ||||||
| Spring steels | ≤ 350 HB | 11 | 0,040 | 0,050 | 0,060 | 0,060 |